

Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
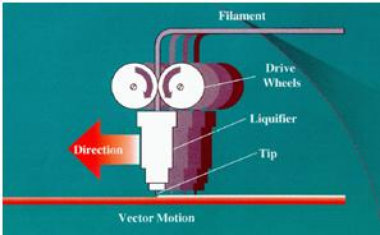
(FDM) is an additive manufacturing technology commonly used for modeling, prototyping, and production applications. FDM works on an "additive" principle by laying down material in layers.
In this technique, filaments of heated thermoplastic are extruded from a tip that moves in the x-y plane. FDM builds plastic models by extruding a semi-molten filament through a heated nozzle in a prescribed pattern onto a platform. The nozzle is moved over the platform in the required geometry of the part which is driven by the CAD data.
The platform is maintained at a lower temperature, so that the thermoplastic quickly hardens. After the platform is lowered, the extrusion head deposits a second layer upon the first layer. The process is repeated until the required object is built. The supports are built along the way which is fastened to the part with a weaker material. Support structures are fabricated for overhanging geometries and are later removed by breaking them away from the object. A Water –soluble support material which can simply be washed away is also available.
The most commonly used materials in this process are Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), polycarbonates, polyenolsulfone and waxes.
Advantages
- High strength and cost-effective process
- Process offers multiple material with greater strength
- Fast process with quick changing of material
Applications
- Fit, form and functional prototypes for testing
- Rapid tooling like investment casting and injection molding
- prototypes constructed for production materials
Limitations
- Rough surface finish and accuracy is less compared to other processes.




